-
Business

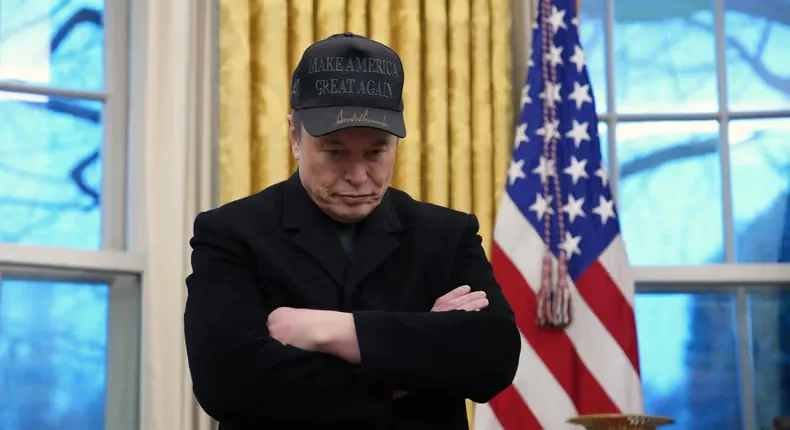
7 Shocking Reasons Tesla Stock Is Falling After Elon Musk’s Political Party Announcement
7 Shocking Reasons Tesla Stock Is Falling After Elon Musk’s Political Party Announcement Tesla stock…
Read More » -

-

-

-

-

Trending
-
Top 10s

Top 10 Richest Musicians in the World 2025
The music industry has always been a lucrative space, but in 2025, the richest musicians in the world have taken wealth accumulation to a whole new level. The top 10 richest musicians in the world…
Read More » -

-

-

-

| # | Coin | Price | Marketcap | Volume (24h) | Supply | Change | Last 24h |
|---|
-
Biography

A Biography of Elon Musk: Early Life, Tech, and Space Vision
Elon Musk is a name synonymous with groundbreaking innovation, technology, and ambitious ventures that continue to redefine industries around the globe. Born on June 28, 1971, in Pretoria, South Africa, Musk’s extraordinary career as an…
Read More »
-
History

History of SpaceX: Revolutionizing Space Exploration
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., widely known as SpaceX, stands as a groundbreaking force in the aerospace industry. Founded by Elon Musk in 2002, SpaceX has transformed humanity’s approach to space exploration, with ambitious goals of…
Read More » -

-

-

-

-
AI

History of ChatGPT: Evolution of AI-Powered Conversations
Discover the history of ChatGPT, its evolution, and how it transformed AI-powered conversations. Learn about its development, milestones, and future prospects. Artificial intelligence (AI) has reshaped how we interact with technology, and one of the…
Read More » -

Faith & Spirituality
-
Faith & Spirituality

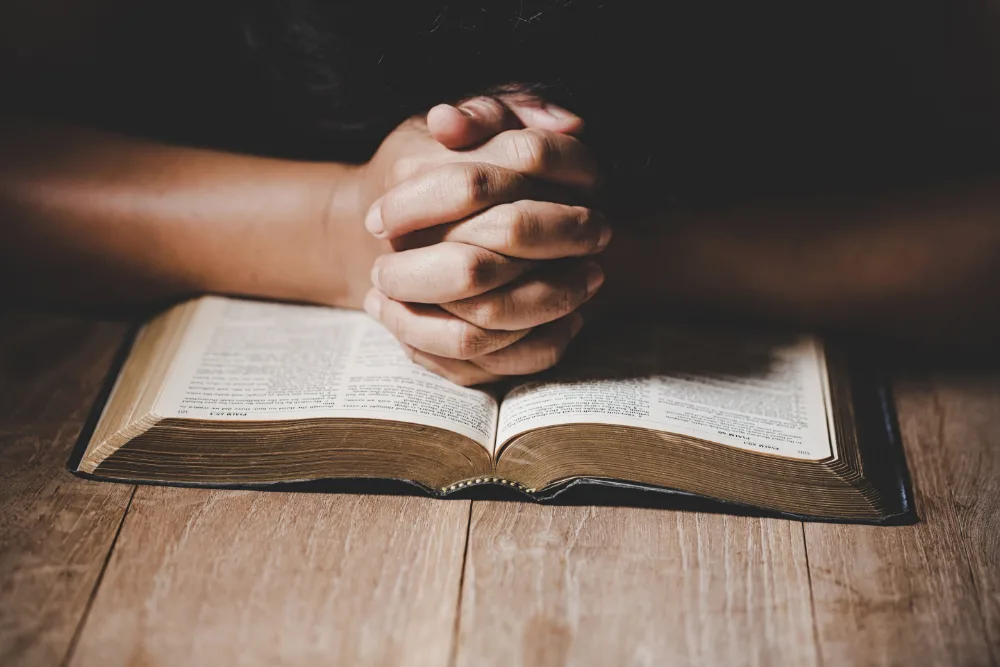
Give Your Life to Christ: A Journey to True Fulfillment
Life is full of choices, and one of the most important decisions you can ever make is to give your life to Christ. This decision isn’t just about changing your habits or joining a church—it’s…
Read More »
-
Politics

U.S. Supreme Court Halts $2B Foreign Aid Payment: Judicial Oversight & Fiscal Policy
The U.S. Supreme Court pauses a lower court’s mandate on $2 billion in foreign aid payments. This article delves into judicial oversight, fiscal policy, and the future of U.S. foreign aid strategy. Introduction: The Supreme…
Read More » -

-

-

-

-
AI

What is Manus Ai and how does it work?
Discover Manus Ai, the groundbreaking autonomous AI agent from China that’s setting new standards in task automation. Learn about its capabilities, performance, and the implications for the future of AI. Imagine a world where your…
Read More » -

-

-

-

-
Technology

Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin vs. Elon Musk’s SpaceX
The competition in space exploration has reached new heights as Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin emerges as a strong contender against Elon Musk’s SpaceX. The aerospace rivalry between these two tech giants is reshaping the future…
Read More »
-
Health

HMPV Virus: Symptoms, Spread, and Prevention Tips
In recent months, a previously lesser-known virus, Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), has captured the attention of global health authorities. With its…
Read More »